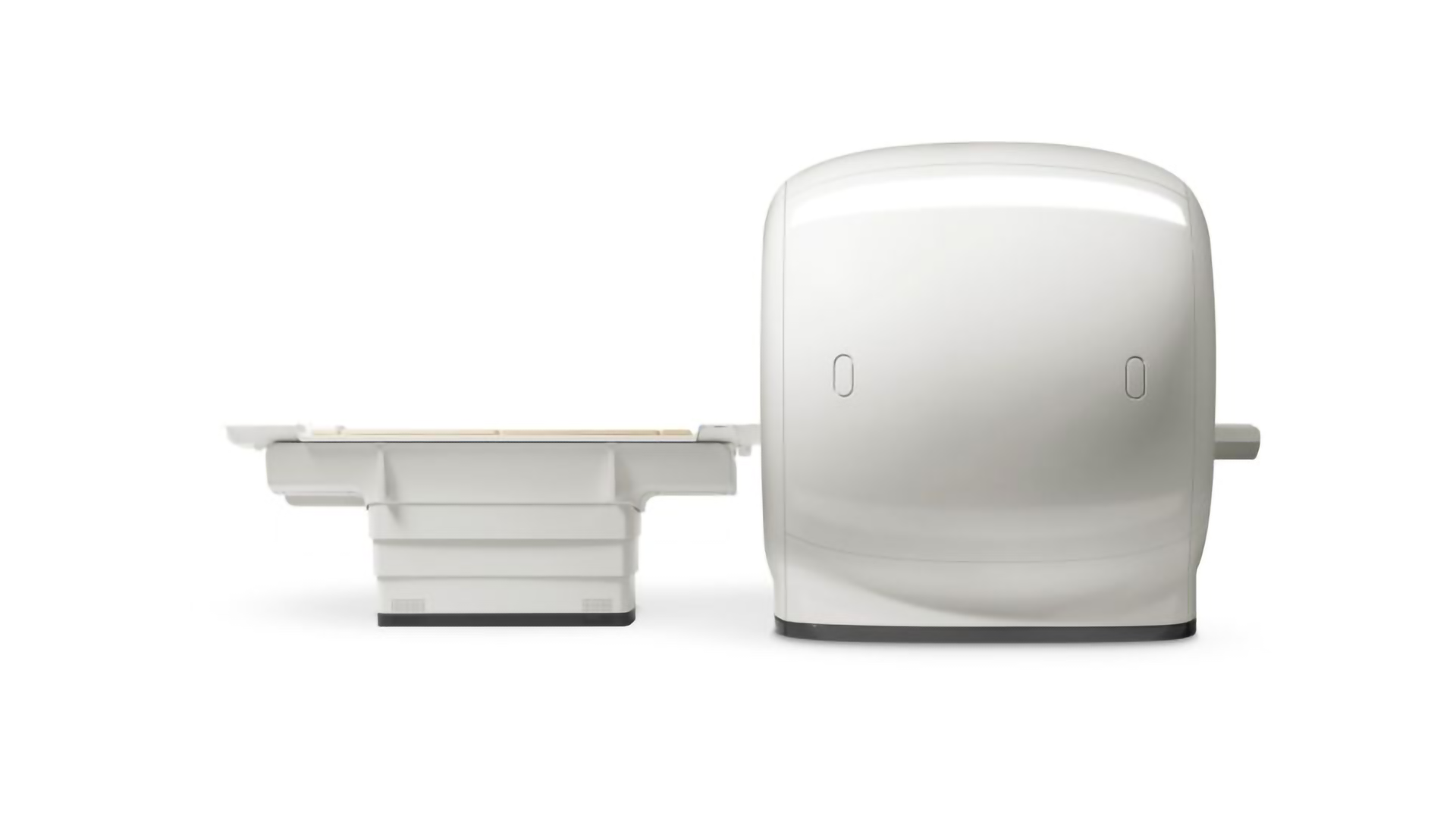
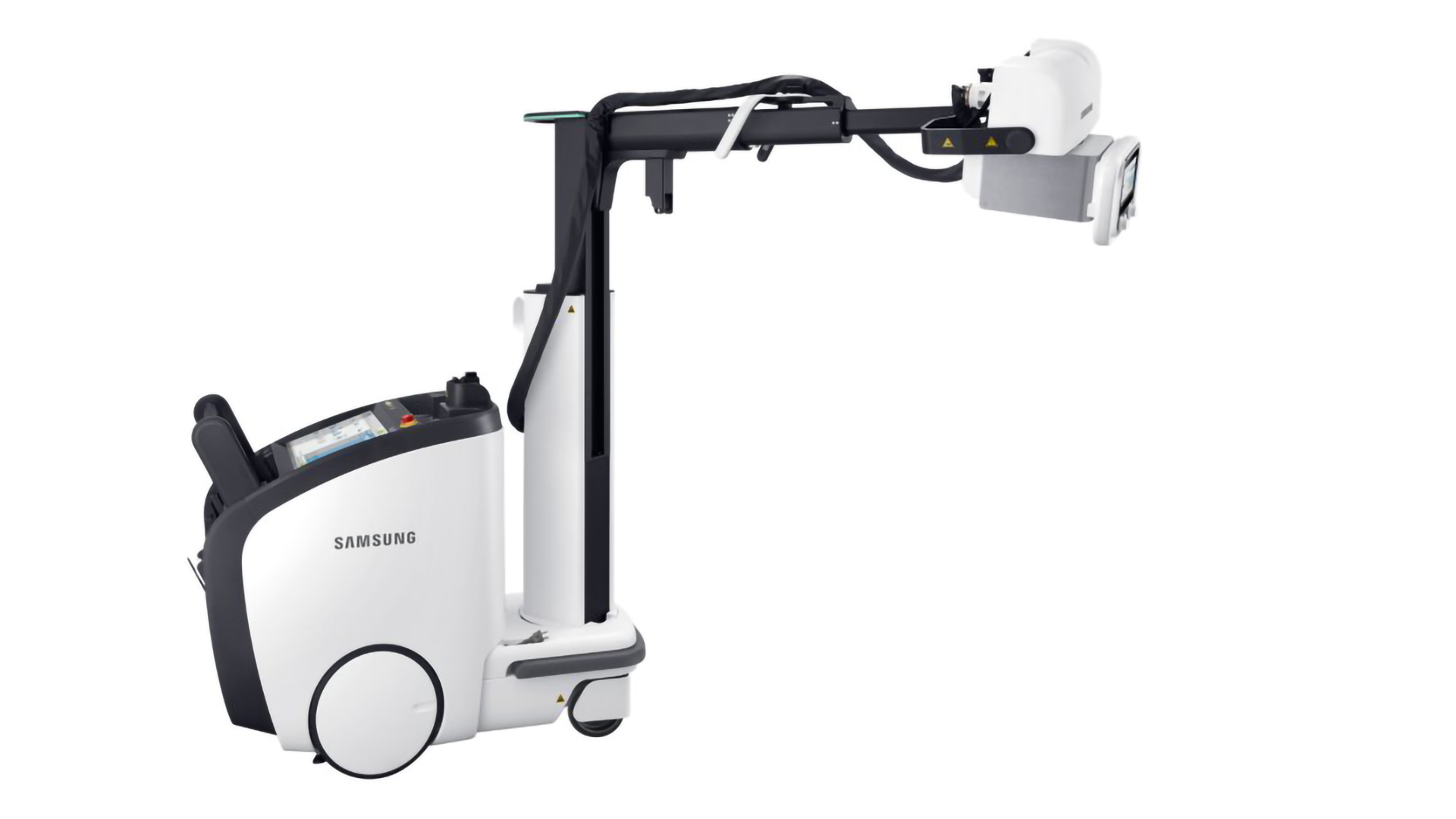
Projectional Radiography (X-Ray)
Video
What
Projectional radiography is the practice of imaging the body's internal structures using X-rays or other forms of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
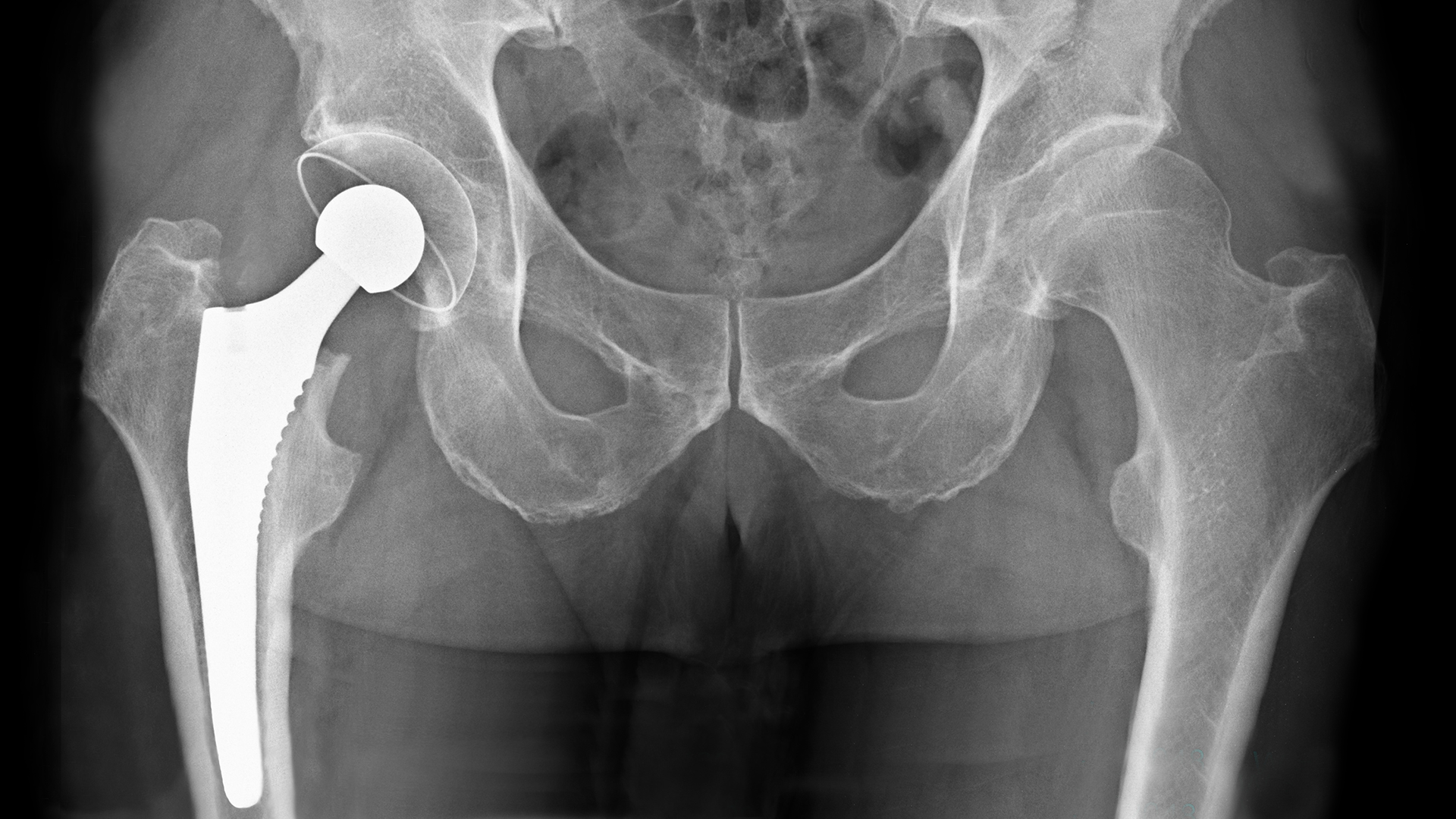
X-Ray of Total Hip Replacement
Why
Projectional radiography is often used for the following purposes:
To look at bones in order to see bone fractures, find bone pathology, and to measure bones for growth studies.
To look at implanted devices such as an artificial knee or hip.
To look for objects in the body that aren't supposed to be there.
To look at soft tissues such as the lungs, heart, bowel, neck, orbits of the skull, and soft tissue trauma resulting from bone fractures.
To look at the teeth and gums.
To look at the breasts to screen for breast cancer and to identify suspicious tissues before a biopsy or a lumpectomy. This specific type of projectional radiography is called mammography.
How
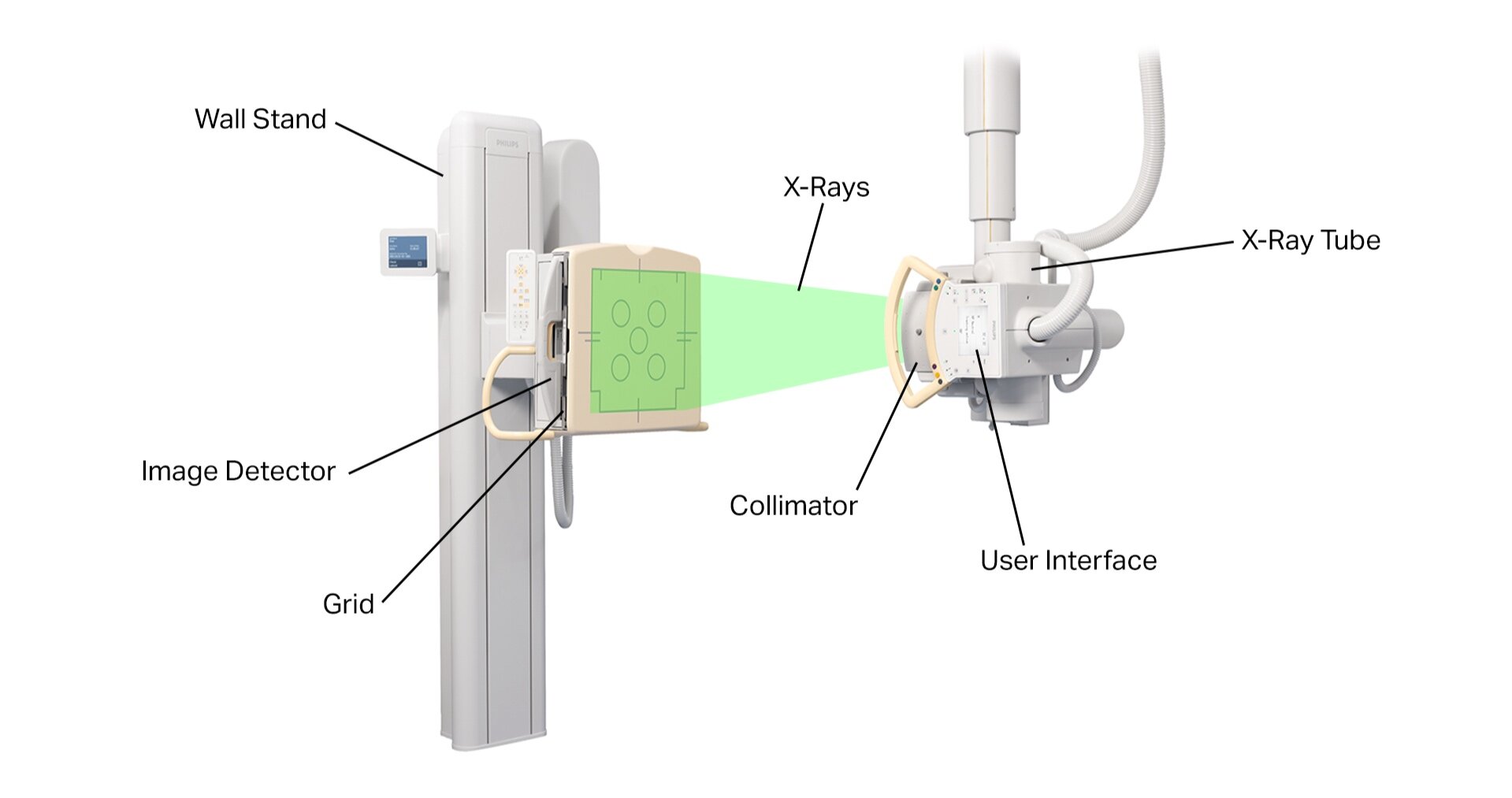
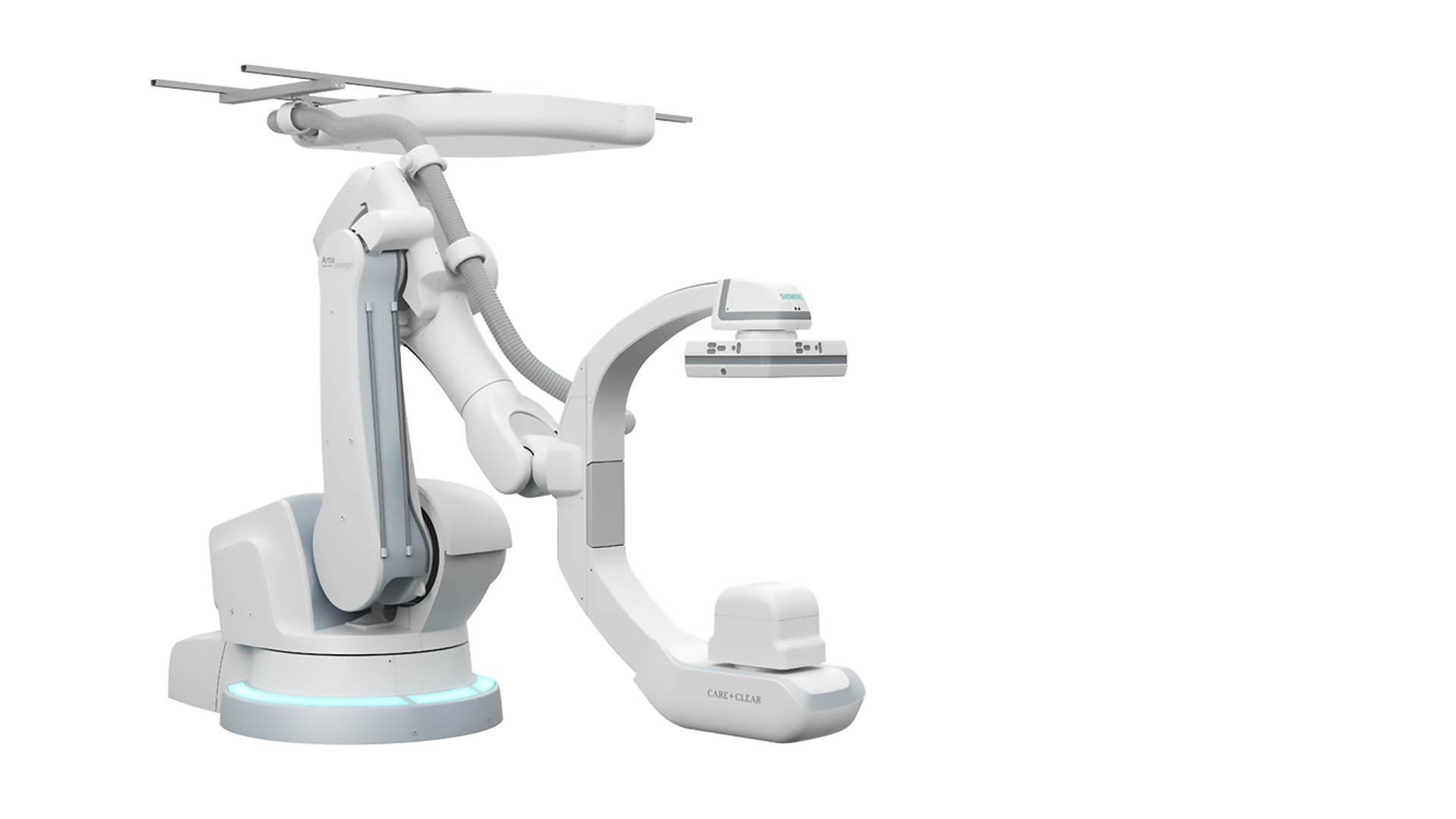
A typical projectional radiography system consists of the following components:
X-Ray Tube: This is what produces the X-rays. An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube which applies a high voltage to accelerate electrons released from a hot cathode to an extremely high velocity. These high-energy electrons collide with a metal anode, producing X-rays. The voltage of the X-ray tube and the material of the anode determine the energy of the resulting X-rays. An anode made of tungsten or a more crack-resistant alloy of rhenium and tungsten is typically used to produce high-energy X-rays up to 150 keV for imaging hard tissues. An anode made of molybdenum is typically used to produce low-energy X-rays down to 5 keV for imaging soft tissues in mammography.
Collimator: This focusses the X-ray beam by allowing only X-rays traveling in a certain direction to pass through.
Patient: The X-rays go through the patient and some of the radiation is absorbed. Denser structures such as bone absorb more X-rays than softer structures.
Table and/or Wall Stand: This is what the patient lays on or stands in front of.
Bucky-Potter Grid: This may be placed between the patient and the image detector to reduce the quantity of scattered X-rays reaching the detector. This improves the contrast resolution of the image but also increases the radiation exposure for the patient.
Image Detector: This is what collects the X-rays that went through the patient to form the image. There are three main types of image detectors. The first type uses X-ray film in combination with an X-ray sensitive screen. The second type uses an image intensifier, which is a vacuum tube coated with caesium iodide that converts the acquired X-ray image into one visible on a video screen. The third type uses digital array detectors, which consist of thin-film transistors that either indirectly detect light emitted from a scintillator material like caesium iodide or directly capture the electrons produced when X-rays hit the detector. Digital detection is becoming the standard image detection method today.
User Interface: This is how the user operates the radiography system.
Processor or Image Reader: This is what the user uses to view and analyze the X-ray images.
Radiocontrast Agent: Projectional radiography is often performed using a radiocontrast agent to improve visibility of the target structures. Common radiocontrast agents include iodine, barium, air, and carbon dioxide.
Components of a Typical Projectional Radiography System
X-Ray Tubes
Image Detectors
Who
Some of the main companies who make projectional radiography systems include:
Fujifilm (FDR)
GE (Definium, AMX)
Philips (DigitalDiagnost, MobileDiagnost)
Siemens (YSIO, MULTIX, SHARP, Luminos, Multitom Rax)
Shimadzu (RADspeed, EZy-Rad)
Canon, Toshiba (Ultimax-i, OMNERA, SOLTUS)
Carestream (DRX)
Hitachi (DR, DX-D)
Samsung (AccE)
References
http://www.usa.philips.com/healthcare/solutions/radiography/radiography, http://www.usa.philips.com/healthcare/solutions/fluoroscopy/fluoroscopy
http://www.fujifilm.com/products/medical/digital_radiography/
http://www3.gehealthcare.com/en/products/categories/radiography
http://www.healthcare.siemens.com/radiography, http://usa.healthcare.siemens.com/fluoroscopy
http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com/products/xray/rx/index.html
http://www.hitachi.com/businesses/healthcare/products-support/xr/index.html
http://www.samsung.com/global/business/healthcare/healthcare/digital-radiography